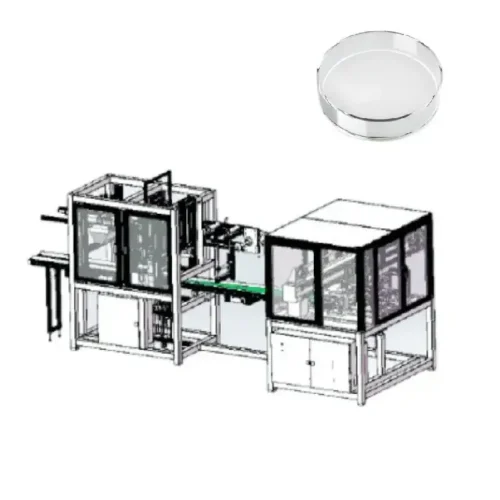
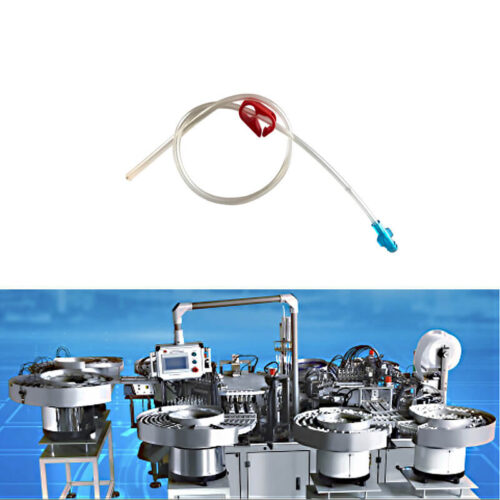
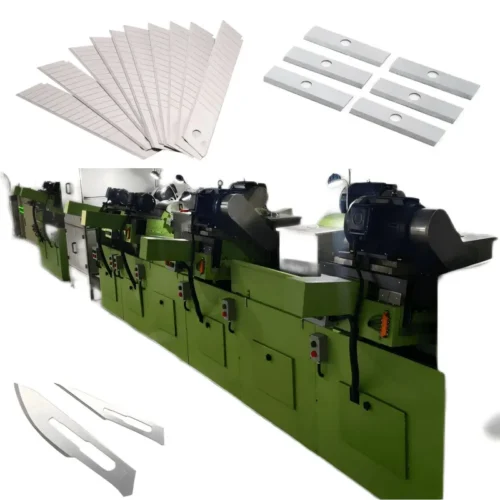
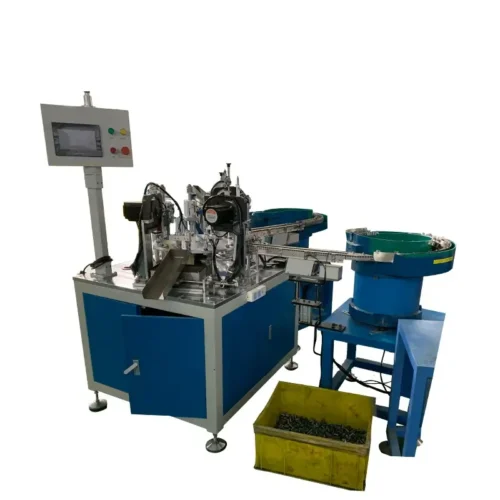
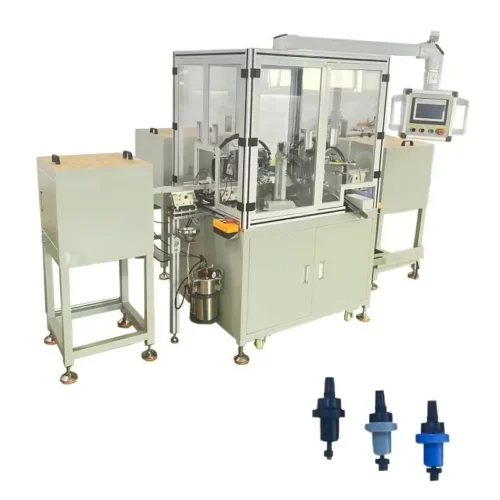
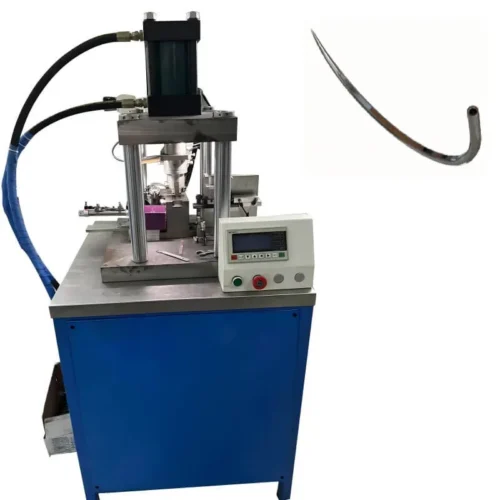
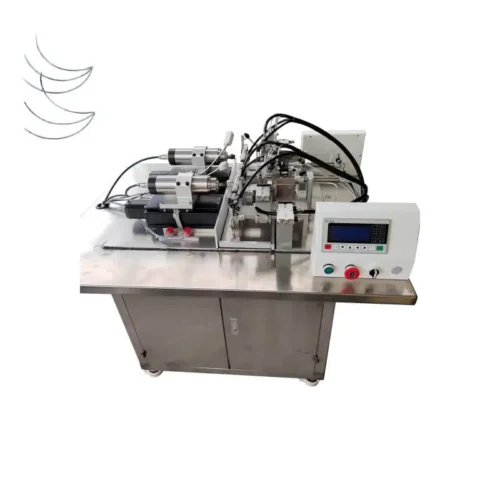
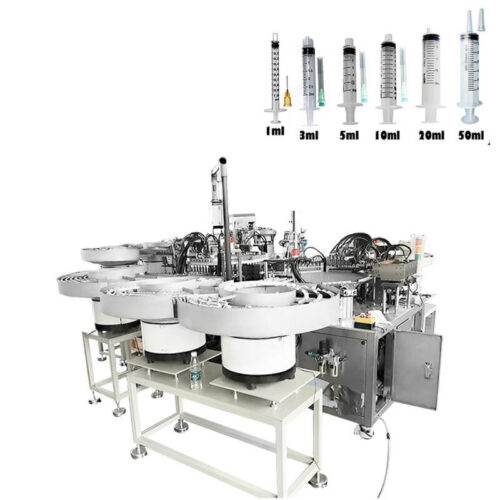
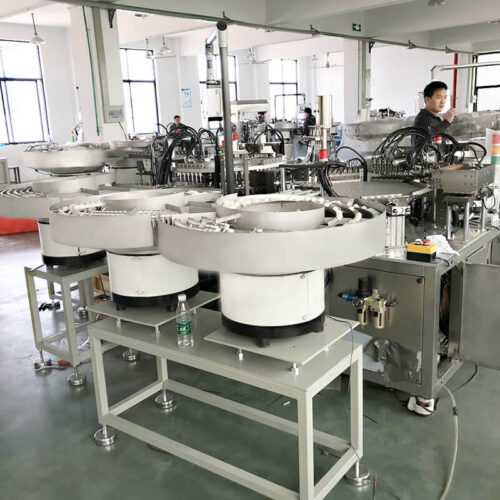
Medical device assembly machines production line?
Feed System:
Equipment used to supply raw materials and components to production lines.
This can include automatic feeders, conveyor belts, and material handling systems, among others.
Processing Equipment:
Machinery for machining, forming, and assembling components.
These devices can vary based on specific medical device needs.
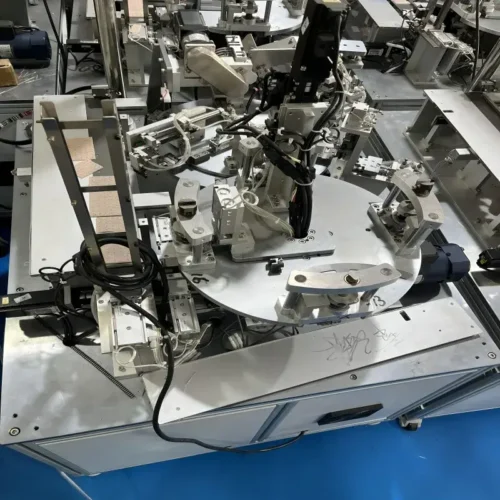
Automated Robots:
Robotic systems for repetitive tasks and precise assembly.
These robots can be programmed according to the requirements of the product and perform tasks such as assembly, packaging, and inspection during the production process.
Quality Control System:
The system can ensure that medical devices manufactured
meet quality standards and regulations.
This can include vision inspection systems, dimensional measuring
equipment, and functional testing equipment, among others.
Data tracking and management system:
A system for recording and managing data and information in the production process.
This can include barcode scanners, RFID technology, and
production data management software, among others.
Outfeed And Packaging System:
Equipment used to remove finished products from the production line and pack them.
This can include automated sorters, packaging machines, and label printers, among others.
What are the advantages of medical device assembly machines?
Improve Efficiency:
Medical device assembly machines automate assembly tasks and
are more efficient than manual operations.
Automating the assembly process can reduce manpower
requirements and assembly time, thereby increasing production efficiency.
Improve Product Quality And Consistency:
Automating the assembly process can ensure the accuracy and
consistency of product assembly and reduce defects due to human error.
Precise machine control ensures that parts are installed and
assembled, improving product quality and reliability.
Reduce Labor Costs And Dependencies:
The use of medical device assembly machines can reduce the need
for manpower, thereby reducing labor costs and associated dependencies.
Compared with manual operation, automated assembly does not
need extra training and supervision, which can reduce personnel input and management work.
Improve Security:
The assembly of some medical devices may involve exposure to
hazardous materials, delicate components, or high-temperature/high-pressure operations.
Automated assembly machines are able to operate in these
environments, reducing the potential risk of injury to operators and improving safety.
Flexibility And Scalability:
Medical device assembly machines can often be adjusted and
configured according to the requirements of different products.
This means that the production line can adapt to the
assembly needs of different products, providing higher production flexibility and scalability.